Business Model Canvas Examples: Google Maps, Airbnb, Uber
Editable template, case studies, and alternatives
In this free post:
Business Model Canvas: Editable Template
Business Model Canvas: Examples
Google Maps
Airbnb
Uber
Business Model Canvas: Cons
Business Model Canvas: Alternatives
Premium: An Editable Notion Template
Business Model Canvas: Editable Template
The Business Model Canvas developed by Strategyzer is not just a business model. It combines elements of strategy and business model. As the authors state, it’s a “strategic management and entrepreneurial tool.”
Business Model Canvas: Examples
Example 1: Business Model Canvas for Google Maps
Google Maps, one of the most widely used navigation apps globally, offers a comprehensive mapping service that integrates real-time traffic updates, street views, and detailed geographical information.
Its business model is built around providing reliable and user-friendly navigation solutions while monetizing through various revenue streams.
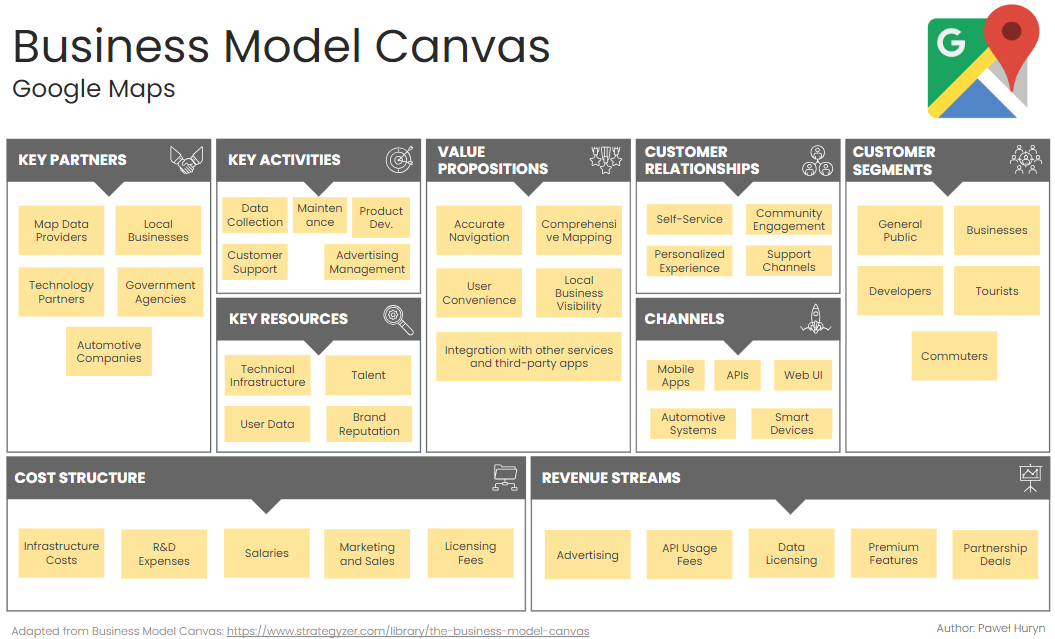
1. Key Partners:
Map Data Providers: Companies and organizations that supply geographical data, satellite imagery, and traffic information.
Local Businesses: Partnerships with local businesses for advertising and featured listings.
Technology Partners: Companies that provide cloud services, APIs, and other technological support.
Government Agencies: Collaboration for access to public infrastructure data and regulations.
Automotive Companies: Partnerships for integrating Google Maps into vehicle navigation systems.
2. Key Activities:
Map Data Collection and Updating: Gathering and updating geographical data, traffic information, and user-generated content.
Product Development: Enhancing features such as navigation, real-time traffic updates, and street view.
Advertising Management: Managing and optimizing ad placements and sponsored listings.
Customer Support: Providing support for users and businesses using Google Maps.
Platform Maintenance: Ensuring the reliability and scalability of the Google Maps platform.
3. Key Resources:
Technical Infrastructure: Data centers, servers, and cloud computing resources.
Talent: Engineers, designers, product managers, and data scientists.
User Data: Anonymized user data to improve service accuracy and personalized experiences.
Brand and Reputation: Google’s strong brand and trust among users.
4. Value Propositions:
Accurate Navigation: Reliable directions and real-time traffic updates.
Comprehensive Mapping: Detailed maps with a wide range of geographical information.
User Convenience: Easy-to-use interface with features like voice navigation and offline maps.
Local Business Visibility: Platform for businesses to advertise and increase visibility.
Integration: Seamless integration with other Google services and third-party applications.
5. Customer Relationships:
Self-Service: Users can access and use Google Maps without direct interaction with Google.
Community Engagement: Users contribute to the platform through reviews, photos, and map edits.
Personalized Experience: Tailored recommendations and routes based on user preferences and history.
Support Channels: Online help centers, forums, and customer support for troubleshooting and feedback.
6. Channels:
Mobile Apps: Google Maps app available on iOS and Android.
Web Interface: Accessible through any web browser.
APIs: Google Maps API for integration with third-party apps and services.
Automotive Systems: Embedded in car navigation systems.
Smart Devices: Integration with smart devices like Google Home.
7. Customer Segments:
General Public: Individuals using Google Maps for personal navigation and location searches.
Businesses: Local businesses and enterprises leveraging Google Maps for advertising and visibility.
Developers: Companies and developers using Google Maps API to enhance their own applications.
Tourists: Travelers seeking directions, local attractions, and services.
Commuters: Daily commuters relying on real-time traffic updates and efficient route planning.
8. Cost Structure:
Infrastructure Costs: Maintaining servers, data centers, and cloud services.
R&D Expenses: Continuous improvement and development of new features.
Salaries: Compensation for employees across various departments.
Marketing and Sales: Promoting the service and acquiring new users and business partners.
Licensing Fees: Payments to data providers and third-party services.
9. Revenue Streams:
Advertising: Revenue from local business ads and sponsored listings.
API Usage Fees: Fees charged to developers and businesses using the Google Maps API.
Data Licensing: Selling anonymized data insights to businesses and researchers.
Premium Features: Subscription fees for advanced features and enterprise solutions.
Partnership Deals: Revenue from strategic partnerships and collaborations.
Example 2: Business Model Canvas for Airbnb
Airbnb revolutionized the hospitality industry by connecting travelers with hosts offering unique accommodations worldwide.
Its platform enables property owners to monetize their spaces while providing travelers with diverse lodging options beyond traditional hotels.
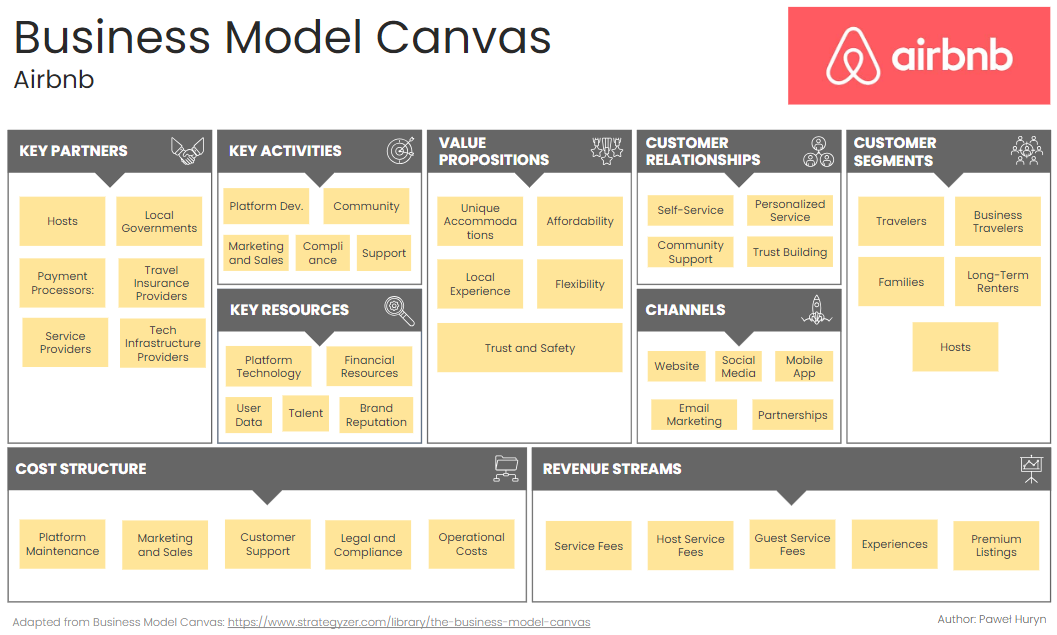
1. Key Partners:
Hosts: Property owners and renters who list their spaces on Airbnb.
Local Governments: Collaborations to ensure compliance with local regulations and laws.
Payment Processors: Companies like Stripe and PayPal for secure payment transactions.
Travel Insurance Providers: Partners offering insurance options for hosts and guests.
Service Providers: Cleaning services, photographers for property listings, and maintenance services.
Tech Infrastructure Providers: Cloud service providers and other tech partners.
2. Key Activities:
Platform Development: Continual development and enhancement of the Airbnb platform.
Marketing and Sales: Attracting hosts and guests through various marketing channels.
Customer Support: Providing support for hosts and guests for a seamless experience.
Community Engagement: Building and maintaining a community of trust among users.
Compliance and Safety: Ensuring properties and transactions comply with local laws and safety standards.
3. Key Resources:
Platform Technology: The Airbnb website and mobile app.
User Data: Data on user preferences, behaviors, and transactions.
Brand Reputation: Strong global brand recognition and trust.
Human Resources: Talented employees in tech, marketing, customer support, and compliance.
Financial Resources: Funds for operational costs, marketing, and growth initiatives.
4. Value Propositions:
Unique Accommodations: A wide range of lodging options from single rooms to entire homes, offering unique experiences.
Affordability: Competitive pricing compared to traditional hotels.
Local Experience: Authentic local experiences through stays with local hosts.
Flexibility: Flexible booking options for both short and long-term stays.
Trust and Safety: Secure payment system, verified profiles, and reviews for trust.
5. Customer Relationships:
Self-Service: Easy-to-use platform for booking and listing properties.
Personalized Service: Personalized recommendations and tailored experiences.
Community Support: Host and guest support via help centers, forums, and customer service.
Trust Building: Reviews, ratings, and verified profiles to build trust among users.
6. Channels:
Website: The primary platform for booking and listing properties.
Mobile App: Accessible on iOS and Android for on-the-go use.
Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter for marketing and community engagement.
Email Marketing: Regular newsletters and promotional emails to users.
Partnerships: Collaborations with travel agencies, tourism boards, and other travel-related businesses.
7. Customer Segments:
Travelers: Individuals and groups seeking unique lodging options.
Business Travelers: Professionals needing short-term accommodations for work trips.
Families: Families looking for spacious and family-friendly accommodations.
Long-Term Renters: Individuals seeking longer stays, such as digital nomads or temporary relocations.
Hosts: Property owners and renters looking to monetize their extra space.
8. Cost Structure:
Platform Maintenance: Costs associated with developing and maintaining the Airbnb platform.
Marketing and Sales: Expenses for attracting new hosts and guests.
Customer Support: Costs of providing support to users.
Legal and Compliance: Ensuring compliance with local laws and regulations.
Operational Costs: Day-to-day operations, including salaries and administrative expenses.
9. Revenue Streams:
Service Fees: Fees charged to guests and hosts for each booking.
Host Service Fees: A percentage of the booking fee charged to hosts.
Guest Service Fees: A percentage of the booking fee charged to guests.
Experiences: Revenue from Airbnb Experiences, where hosts offer activities and tours.
Premium Listings: Fees for premium placement or featured listings on the platform.
Example 3: Business Model Canvas for Uber
Uber has transformed urban transportation by offering a convenient and efficient ride-sharing service accessible through a mobile app.
Its business model focuses on connecting drivers with riders, ensuring competitive pricing, and maintaining high service quality through advanced technology and extensive partnerships.
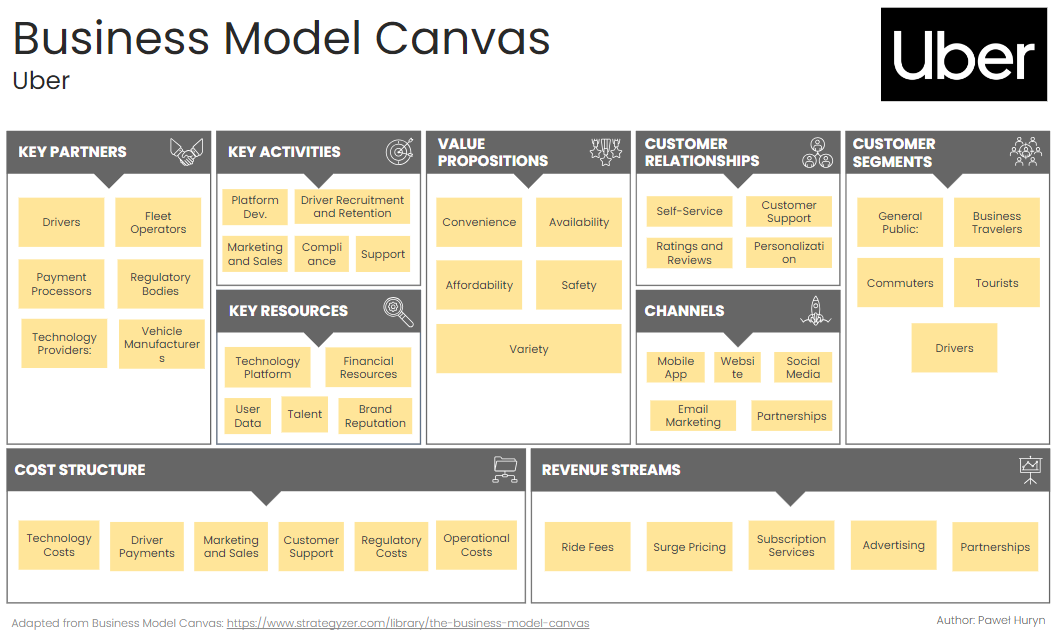
1. Key Partners:
Drivers: Independent contractors who use their own vehicles to provide rides.
Fleet Operators: Companies that provide vehicles and drivers for Uber's various services.
Payment Processors: Financial partners like PayPal and credit card companies for handling transactions.
Regulatory Bodies: Government agencies ensuring compliance with local transportation laws.
Technology Providers: Partners providing mapping, GPS, and other technological infrastructure.
Vehicle Manufacturers: Partnerships for vehicle leasing and purchase deals for drivers.
2. Key Activities:
Platform Development: Continuous development and maintenance of the Uber app and backend systems.
Marketing and Sales: Attracting drivers and riders through advertising and promotional activities.
Customer Support: Providing assistance to both riders and drivers.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with local, regional, and national regulations.
Driver Recruitment and Retention: Strategies to attract and keep drivers on the platform.
3. Key Resources:
Technology Platform: The Uber app and backend systems.
User Data: Data on rider and driver behavior and preferences.
Brand Reputation: Strong global brand presence and recognition.
Human Resources: Skilled employees in technology, marketing, and operations.
Financial Resources: Capital for operations, marketing, and expansion.
4. Value Propositions:
Convenience: Easy booking of rides via the app.
Availability: Wide availability of rides at any time.
Affordability: Competitive pricing compared to traditional taxi services.
Safety: Background checks for drivers, GPS tracking, and in-app safety features.
Variety: Different ride options (e.g., UberX, UberPOOL, UberBLACK) to suit various needs and budgets.
5. Customer Relationships:
Self-Service: App-based booking and payments without the need for direct interaction.
Customer Support: 24/7 support through the app for both riders and drivers.
Ratings and Reviews: Two-way rating system to maintain service quality and trust.
Personalization: Personalized ride suggestions and promotions based on user behavior.
6. Channels:
Mobile App: Primary platform for booking rides, available on iOS and Android.
Website: Information about services and company.
Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram for engagement and promotion.
Email Marketing: Newsletters and promotional emails to users.
Partnerships: Collaborations with other businesses and services to expand reach.
7. Customer Segments:
General Public: Individuals needing rides for various purposes.
Business Travelers: Professionals needing reliable transportation for work-related travel.
Commuters: Daily commuters looking for convenient and cost-effective transport options.
Tourists: Visitors needing transportation in unfamiliar cities.
Drivers: Individuals looking to earn income through ride-sharing.
8. Cost Structure:
Technology Costs: Development and maintenance of the Uber app and infrastructure.
Driver Payments: Earnings paid out to drivers.
Marketing and Sales: Costs for advertising, promotions, and customer acquisition.
Customer Support: Expenses related to providing 24/7 support.
Regulatory Costs: Expenses related to compliance with transportation laws.
Operational Costs: General administrative and operational expenses.
9. Revenue Streams:
Ride Fees: Commission from each ride booked through the platform.
Surge Pricing: Additional revenue from higher fares during peak demand times.
Subscription Services: Fees from services like Uber Pass or Uber for Business.
Advertising: Revenue from in-app advertising and promotions.
Partnerships: Revenue from strategic partnerships and integrations with other services.
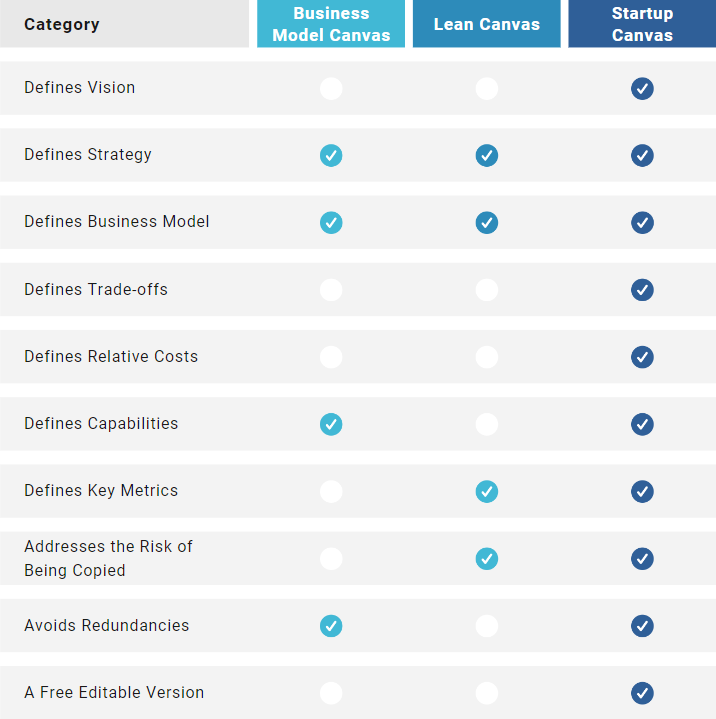
Business Model Canvas: Cons
While the Business Model Canvas is the most popular canvas for a new product, what could be improved:
It doesn’t mention a vision. Why are we doing this? Why should your employees wake up every day and go to work? It's especially critical for startups, founders included.
It doesn’t mention that you should ensure that your competitors can’t/won’t copy your strategy without sacrificing their existing businesses. That's essential. The moment you succeed, someone will try to do the same.
It doesn’t mention trade-offs, which are the things you don’t want to do. They are particularly important for startups, where it’s often tempting to capture every possible opportunity. Trade-offs create focus.
It doesn’t mention key metrics. How will you test if your strategy and business model are working?
It doesn’t mention relative costs, which are an essential strategic choice. Consider Apple vs. Xiaomi.
It doesn’t explain what a Value Proposition really is. In addition, Value Proposition Canvas also doesn’t make that clear. Read more.
In my opinion, “Customer Relationships” and “Key Activities” are unnecessary. Virtually no one uses the former, and the latter could be included in the Can’t/Won’t section. If it existed.
Business Model Canvas: Alternatives
Business Model Canvas is not the only available tool. Depending on what you are looking for, you might also consider:
For a new product:
Startup Canvas (Product Strategy and a Business Model for a new product)
Lean Canvas (File > Download)
For an existing product, a better choice will be:
Premium: An Editable Notion Template
My premium subscribers can access a Notion template that they can easily duplicate to their Notion account.
Our premium PM resources: https://www.productcompass.pm/p/your-premium-pm-resources